Like many industries and areas of technology, the cybersecurity sector is prone to using jargon, technical terms, and acronyms that can confuse even the most seasoned industry insider. We work with businesses and public sector organizations all over the world and during our many meetings and interactions, we invariably get asked at least once, ‘what is that?’
To try and head off any confusion, we are launching a series of blog posts that aim to explain precisely what we mean by certain industry terms and phrases. Others may have a slightly different interpretation, but this is ours and we are sticking to it.
First up – what is Adaptive Redaction?
Addressing the ever-evolving cyber threat
For most organizations, ensuring they are well-protected against cyber-attacks and accidental data loss is, from a data security point of view, their biggest priority. They have seen the damage and disruption that can be caused by a data breach, and they will have noted the heavy financial penalty if they are found to be non-compliant with GDPR, not to mention the flood of compensation claims and loss of reputation that can follow.
To combat the variety and volume of cyber risks faced by the organization, defensive measures are put in place. Some of these security solutions ‘stop and block’ any email, web or endpoint transfers deemed to have risk implications. Such measures certainly keep the business secure, but they also impact the efficiency of the day-to-day operations.
For example, the management overhead on the messaging or security IT teams can be significant and when emails and documents are blocked unnecessarily it can delay important business. Overzealous filters can start to frustrate employees, especially when they are chased for documents they may have sent hours ago, and when this happens, they start to find other ways to share information, opening the organization up to more risk.
Finding the balance between the need to protect the organization and the ability to freely collaborate can be difficult to achieve, and that’s what makes Adaptive Redaction such an innovation. It provides the cybersecurity protection needed by today’s organizations but also ensures that employees can get on and do their jobs safely and effectively.
Clearswift Adaptive Redaction
Clearswift was the first company in the world to offer Adaptive Redaction and it is still something that differentiates us from other cybersecurity vendors. Adaptive Redaction involves the identification of critical or confidential information and cyber threats which are either redacted or sanitized to allow the on-going flow of communication – with no disruption.
There are three main options for using Adaptive Redaction:
Text redaction - this covers both inbound and outbound communication and removes the sensitive text in question from emails and documents. Exactly what data is removed depends entirely on an organization’s policy, it can be based on regulation (GDPR, HIPAA), critical data (PCI, PII), keywords (IP or classified projects) or other criteria. Clearswift’s Optical Character Recognition (OCR) functionality even allows the extraction of text from image-based files which are then redacted from the image as well.
Image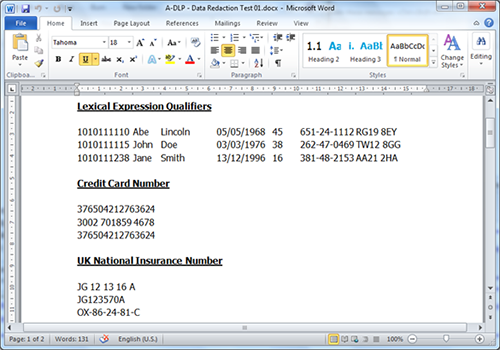
Before
Image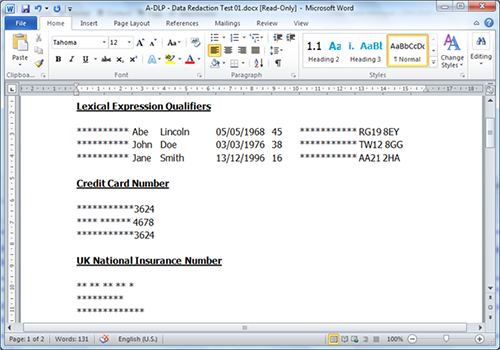
After
Document sanitization - Provides the automated removal of hidden metadata such as comments and revision history, along with the removal of author, username, and server names etc., so that the information can’t be harvested for phishing attacks. Additionally, Clearswift’s solution uses anti-steganography functionality, which means that data hidden in image files can be wiped clean too.
Image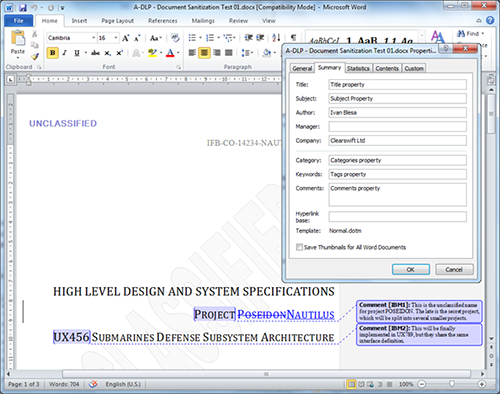 Image
Image
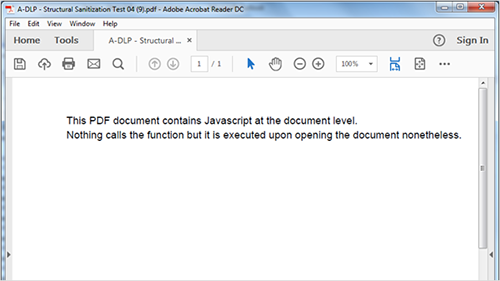
Structural sanitization - this allows for the wholesale removal of any malicious code without any delays to sharing and access. This method of Adaptive Redaction stops embedded macros, scripts, and ransomware from entering a corporate network, whether via phishing emails, drive-by downloads, or attacking uploads.
Image Image
Image