The majority of malicious emails reported in user inboxes contained a link to a phishing site, making credential theft emails the attack method of choice for cybercriminals in Q4. Credential theft made up nearly 60% of all reported incidents, with more than half of the volume attributed to O365 attacks. Despite the threat actor preference toward this threat type, credential theft attacks declined as a whole in Q4, with increased reports of response-based and malware attacks reaching inboxes.
Every quarter, Fortra analyzes hundreds of thousands of email phishing attacks targeting enterprises, their brands, and their employees. In this post, we take a look at phishing activity targeting organizations, their brands, and customers.
Employee Reported Emails
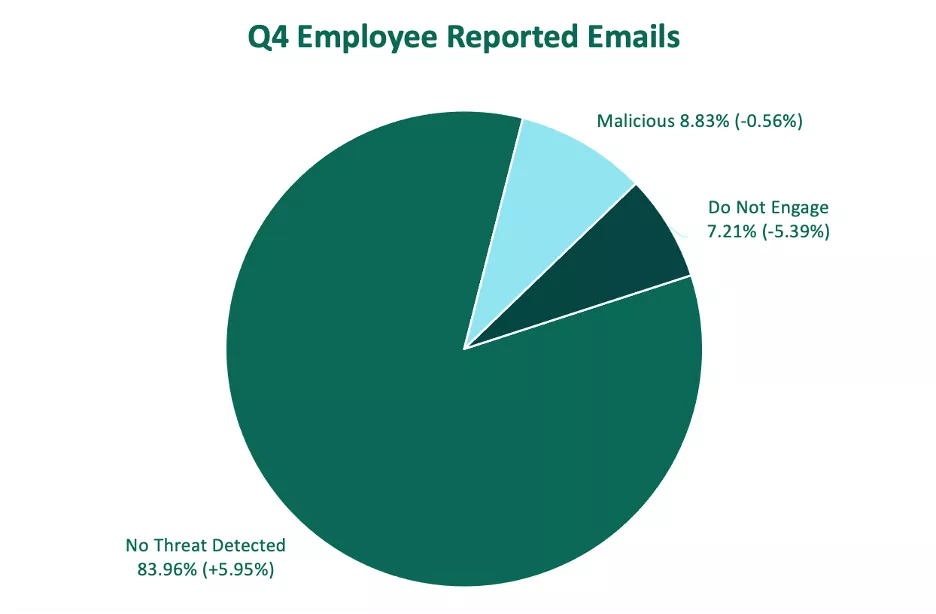
In Q4, employee-reported emails classified as malicious and as untrustworthy (Do Not Engage) both declined over the previous quarter. Despite this, year-over-year, emails explicitly deemed malicious in 2023 exceeded 2022 volume.
Reported emails containing no threat increased in volume, representing nearly 84% of total volume.
Top Email Threat Categories
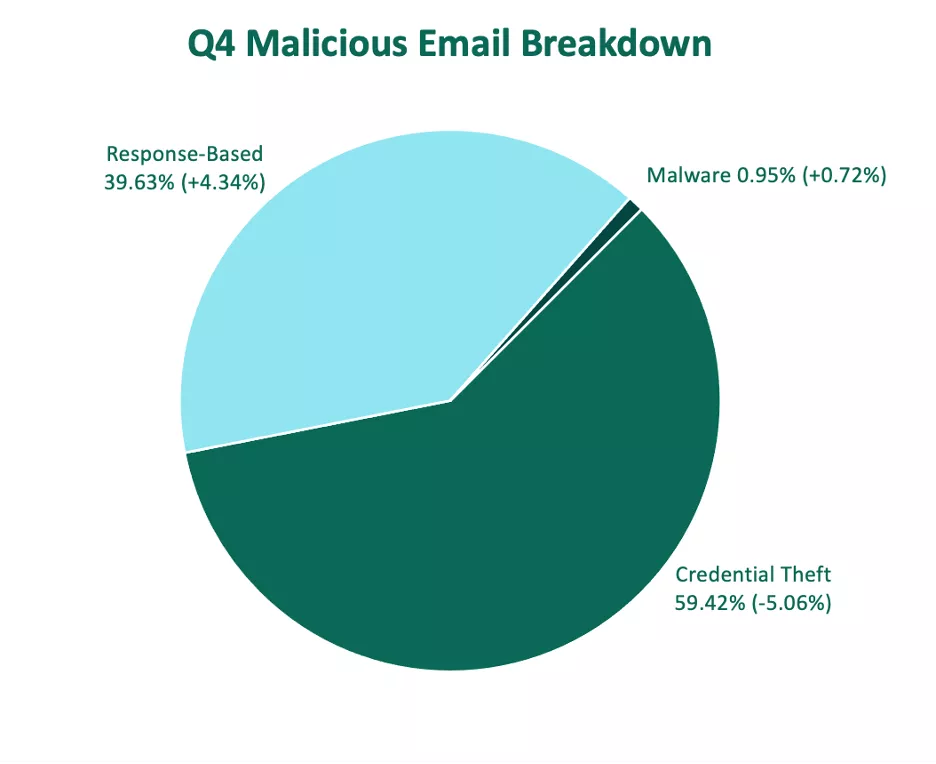
Credential Theft Attacks
Credential theft was the most reported email threat type in Q4, despite a more than 5% decline over the previous quarter. End users have identified credential theft more than any other threat type in 2023, with response-based and malware attacks less likely to be reported to security teams. This is in contrast to the latter half of 2022, when response-based attacks such as 419 and hybrid vishing specifically were flagged at a high rate by end users.
Fortra breaks credential theft into two categories:
- Phishing links that direct email users to malicious websites
- Phishing attachments that direct email users to malicious websites
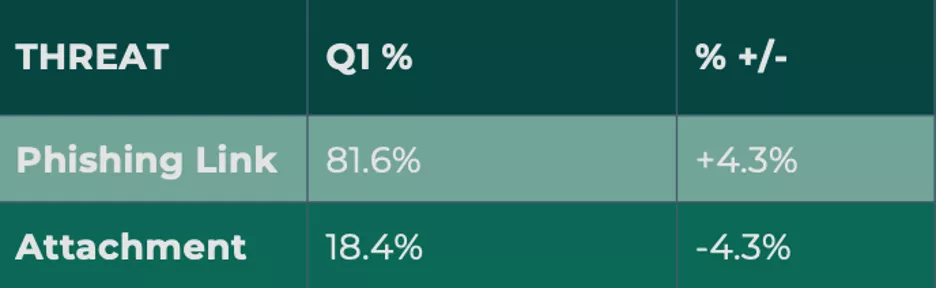
In Q4, credential theft attacks containing a malicious link grew to 81.6%, reaching its highest share of volume in more than a year. The majority of those took the form of Office 365 phish. O365 attacks have increasingly burdened security teams over the course of 2023, with reported activity peaking in Q4 at 52.8% share of all credential theft incidents.
Phishing attachments declined 4.3% in Q4.
Response-Based Attacks
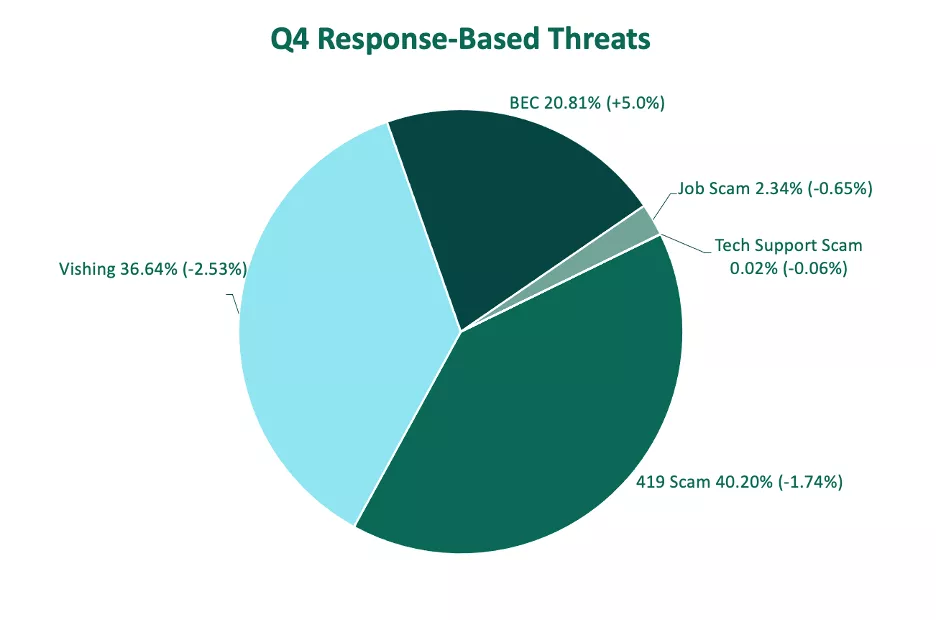
Emails considered response-based increased more than 4% in Q4, representing 39.6% of all reported emails. Within the group, 419 attacks (advance-fee fraud) were reported most, with 40% of activity. Although 419 attacks are historically the top response-based attack of choice for threat actors, they have maintained only a narrow majority over hybrid vishing in Q2, Q3, and Q4 of 2023.
Hybrid vishing or, emails containing a phone number lure within the message body, were the second most reported threat type in Q4, despite a decline of 2.5%. Hybrid vishing made up 36.6% of share of response-based reports. This is the lowest volume recorded since Q2 2022.
In contrast, Business Email Compromise (BEC) reports jumped to nearly their highest volume in two years over the course of Q4. BEC incidents grew 5% QoQ, making up more than 20% of total share response-based attacks.
Job scams and tech support scams both declined in Q4, making up 2.34% and 0.02% of response-based reports, respectively.
Malware Attacks
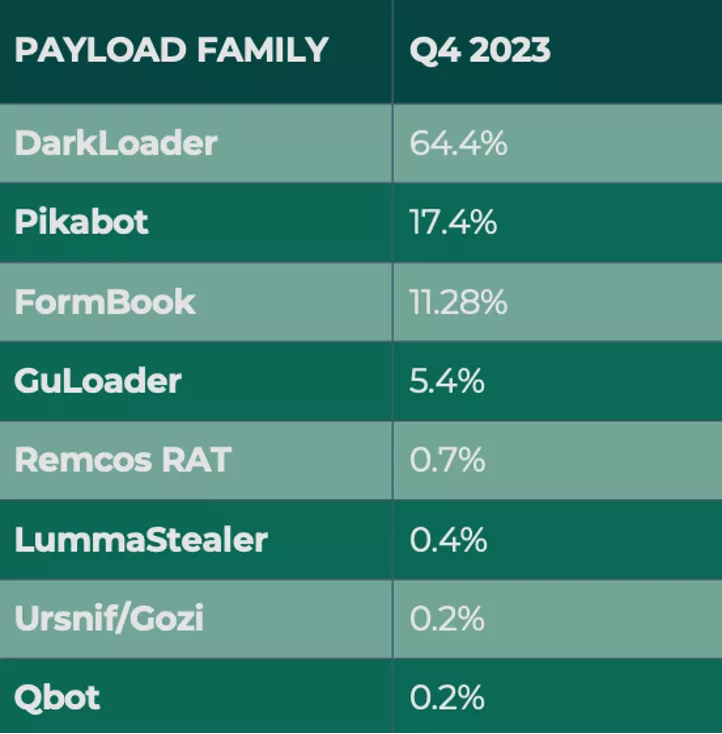
Malware reports grew in Q4, making up just under one percent of all malicious email activity. While malware volume is traditionally minimal when compared to a credential theft or response-based attack, the damage inflicted by this threat type can be swift and difficult to recover from.
DarkLoader, Pikabot, and Formbook made up more than 93% of payload volume in Q4. The most used was DarkLoader, with 64.4% of reports. First discovered in 2017, DarkLoader is a MaaS available on the dark web with a full suite of capabilities including privilege escalation, keylogging, hidden network computing, and browser-stealing.
Pikabot represented 17.4% of volume, making it the second most reported payload. It is known for its advanced evasion techniques and uses language-based cessation to self-terminate. Q4 is the first time that Pikabot has been reported by Fortra clients.
More than 11% of reported payloads delivered the FormBook malware. First detected in 2016, FormBook features include process injection, credential harvesting, screenshot grabs, and is considered a relatively affordable infostealer available through as-a-service models.
In Q4, end users were targeted most by credential theft attacks containing phishing links, despite declining in volume over Q3. Second place response-based attacks were reported more than they were in Q3, with threat-types 419 scams and hybrid vishing making up nearly 80% of the category’s volume. Malware reports also increased, with the DarkLoader family picking up the slack formerly filled by the currently-defunct QBot group. In order to proactively protect against email threats targeting user inboxes, organizations should be cognizant of the types of attacks criminals are launching and tactics associated with each.
Learn how Fortra can help protect against malicious emails targeting your organization with our Cloud Email Security Solution.